Trace and Evaluate Models and RAG Apps with Arize
This guide walks you through how to integrate Arize with your LLMs or RAG applications to trace model activity and evaluate performance in real-time. By instrumenting your app with Arize, you can capture detailed logs, monitor predictions, and analyze model behavior across inputs — making it easier to debug, iterate, and improve accuracy.
We’ll look at how to integrate Arize and Phoenix (its open-source offering) to enable instrumentation. This includes both tracing and evaluations using Arize and Phoenix.
Once you have a Union account, install union:
pip install unionExport the following environment variable to build and push images to your own container registry:
# replace with your registry name
export IMAGE_SPEC_REGISTRY="<your-container-registry>"Then run the following commands to run the workflow:
$ git clone https://github.com/unionai/unionai-examples
$ cd unionai-examples
$ union run --remote <path/to/file.py> <workflow_name> <params>The source code for this example can be found here.
Tracing
LLM tracing records the paths taken by requests as they propagate through various components or steps in an LLM application. Tracing can be enabled for models, RAG apps, and agents.
We’ll start by pulling a model from Hugging Face and storing it as a Union artifact. This acts as a cache and helps avoid network overhead for future deployments of the same model.
Next, we define a VLLMApp to deploy the cached model using vLLM.
Be sure to specify the model artifact URI from the previous step in the app’s spec.
The stream_model=True argument streams the model directly from the artifact to the GPU,
bypassing disk I/O. This significantly speeds up model loading during deployment.
import os
from contextlib import asynccontextmanager
import union
from fastapi import FastAPI
from flytekit.extras.accelerators import L4
from union import Resources
from union.app import App, ArizeConfig, Input, PhoenixConfig
from union.app.llm import VLLMApp
from utils import EmbeddingConfig, VectorStoreConfig
ARIZE_ORG_ID = "<YOUR_ARIZE_ORG_ID>"
ARIZE_SPACE_ID = "<YOUR_ARIZE_SPACE_ID>"
ARIZE_MODEL_ID = "<YOUR_ARIZE_MODEL_ID>"
LLM = "deepseek-ai/DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-1.5B"
MODEL_ID = "deepseek-qwen-1.5b"
PHOENIX_ENDPOINT = "https://app.phoenix.arize.com"
PHOENIX_PROJECT = "phoenix-union"
llm_image = union.ImageSpec(
name="vllm-deepseek",
packages=[
"union[vllm]==0.1.181",
],
apt_packages=["build-essential"],
builder="union",
)
deepseek_app = VLLMApp(
name="vllm-deepseek",
container_image=llm_image,
# TODO: add the model artifact uri
model="<YOUR_MODEL_ARTIFACT_URI>",
model_id=MODEL_ID,
scaledown_after=1200,
stream_model=True,
limits=Resources(mem="23Gi", gpu="1", ephemeral_storage="20Gi", cpu="6"),
accelerator=L4,
requires_auth=False,
)We define a Gradio app with a chatbot-style UI that interacts with a deployed model. The model is hosted using Union, so your data remains private and never leaves your environment or hits third-party APIs.
Using query_endpoint(public=False), we retrieve the internal model endpoint, which the Gradio app calls behind the scenes.
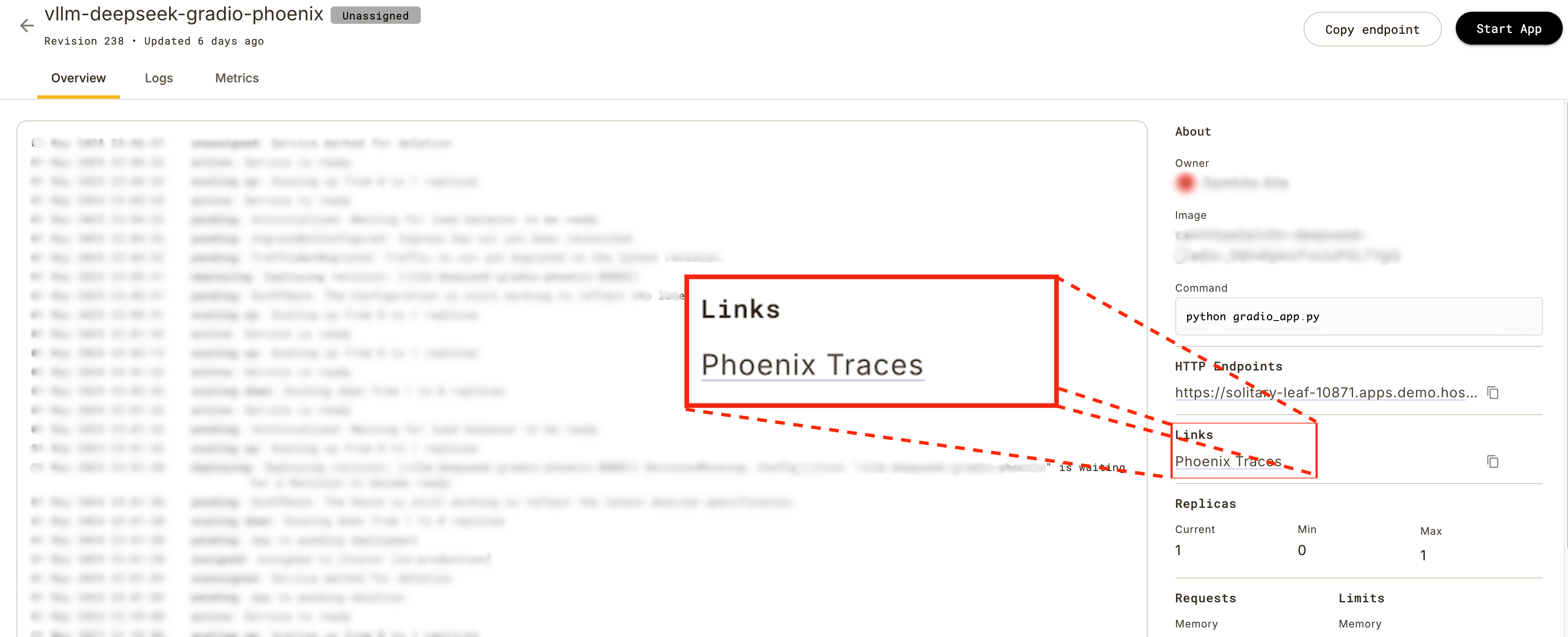
We use PhoenixConfig to generate a link to the Phoenix dashboard. This link appears in the app UI,
allowing you to view trace data directly and gain end-to-end observability of model behavior.
gradio_image = union.ImageSpec(
name="vllm-deepseek-gradio-phoenix",
packages=[
"gradio==5.23.3",
"union-runtime>=0.1.17",
"openinference-instrumentation-openai==0.1.23",
"opentelemetry-semantic-conventions==0.52b1",
"openai==1.71.0",
"arize-phoenix==8.22.1",
],
builder="union",
)
gradio_app = App(
name="vllm-deepseek-gradio-phoenix",
inputs=[
Input(
name="vllm_deepseek_endpoint",
value=deepseek_app.query_endpoint(public=False),
env_var="VLLM_DEEPSEEK_ENDPOINT",
),
],
container_image=gradio_image,
limits=union.Resources(cpu="1", mem="1Gi"),
port=8080,
include=["gradio_app.py"],
args=[
"python",
"gradio_app.py",
],
config=PhoenixConfig(endpoint=PHOENIX_ENDPOINT, project=PHOENIX_PROJECT),
secrets=[
union.Secret(
key="phoenix-api-key",
mount_requirement=union.Secret.MountType.ENV_VAR,
env_var="PHOENIX_API_KEY",
)
],
dependencies=[deepseek_app],
)By specifying dependencies in the app spec, Union automatically deploys the model when the Gradio app is deployed. No need to deploy it separately.
You can manage secrets using Union’s secret management system and control the entire app lifecycle directly from code.
You can find the gradio app logic in
gradio_app.py.
Next, we define a FastAPI app that enables tracing for Arize. This app captures traces for the RAG calls and uses the previously hosted model under the hood.
arize_image = union.ImageSpec(
name="rag-fastapi-arize",
packages=[
"llama-index==0.12.28",
"llama-index-embeddings-huggingface==0.5.2",
"llama-index-vector-stores-milvus==0.7.2",
"llama-index-llms-openai-like==0.3.4",
"union-runtime>=0.1.17",
"arize-otel==0.8.1",
"opentelemetry-exporter-otlp==1.32.1",
"fastapi[standard]==0.115.12",
"openinference-instrumentation-llama-index==4.2.1",
],
builder="union",
)We register the tracer in the FastAPI app’s lifespan event and initialize a LlamaIndex instrumentor since the RAG application is built using LlamaIndex.
@asynccontextmanager
async def lifespan(app):
from arize.otel import register
from openinference.instrumentation.llama_index import LlamaIndexInstrumentor
tracer_provider = register()
LlamaIndexInstrumentor().instrument(tracer_provider=tracer_provider)
yieldTo configure ArizeConfig, provide the full endpoint along with your Arize organization, space, and model IDs.
Once set up, a link to Arize Traces similar to the Phoenix Traces link will appear in the app UI.
This tracing integration is built to work with FastAPI-based applications.
fastapi_app = FastAPI(lifespan=lifespan)
arize_app = App(
name="rag-fastapi-arize",
inputs=[
Input(
name="arize_space_id",
# TODO: Provide the Arize space ID when deploying the app using the CLI: `--arize_space-id <YOUR_SPACE_ID>`
value="default",
env_var="ARIZE_SPACE_ID",
),
Input(
name="arize_project_name", value="arize-union", env_var="ARIZE_PROJECT_NAME"
),
Input(
name="vllm_deepseek_endpoint",
value=deepseek_app.query_endpoint(public=False),
env_var="VLLM_DEEPSEEK_ENDPOINT",
),
],
container_image=arize_image,
secrets=[
union.Secret(
key="arize-api-key",
env_var="ARIZE_API_KEY",
mount_requirement=union.Secret.MountType.ENV_VAR,
),
union.Secret(
key="milvus-uri",
env_var="MILVUS_URI",
mount_requirement=union.Secret.MountType.ENV_VAR,
),
union.Secret(
key="milvus-token",
env_var="MILVUS_TOKEN",
mount_requirement=union.Secret.MountType.ENV_VAR,
),
],
config=ArizeConfig(
endpoint=f"https://app.arize.com/organizations/{ARIZE_ORG_ID}/spaces/{ARIZE_SPACE_ID}/models/{ARIZE_MODEL_ID}"
),
framework_app=fastapi_app,
dependencies=[deepseek_app],
limits=union.Resources(cpu="1", mem="5Gi"),
)We define a FastAPI endpoint to serve the RAG application.
The OpenAILike interface allows us to use models that are compatible with the OpenAI API format.
We fetch embeddings from Milvus, using a pre-defined ingestion job available as a Union task. Finally, we retrieve and return the generated response from the RAG pipeline.
You can find the ingestion logic in
ingestion.py.
@fastapi_app.post("/query_rag")
async def query_rag(
prompt: str,
vector_store_config: VectorStoreConfig = VectorStoreConfig(),
embedding_config: EmbeddingConfig = EmbeddingConfig(),
) -> str:
from llama_index.core import Settings, VectorStoreIndex
from llama_index.embeddings.huggingface import HuggingFaceEmbedding
from llama_index.llms.openai_like import OpenAILike
from llama_index.vector_stores.milvus import MilvusVectorStore
Settings.llm = OpenAILike(
model=MODEL_ID,
api_base=f"{os.getenv("VLLM_DEEPSEEK_ENDPOINT")}/v1",
api_key="abc",
)
Settings.embed_model = HuggingFaceEmbedding(model_name=embedding_config.model_name)
milvus_store = MilvusVectorStore(
uri=os.getenv("MILVUS_URI"),
token=os.getenv("MILVUS_TOKEN"),
collection_name=vector_store_config.collection_name,
dim=embedding_config.dimensions,
index_config={
"index_type": vector_store_config.index_type,
"metric_type": "L2",
"params": {"nlist": vector_store_config.nlist},
},
search_config={"nprobe": vector_store_config.nprobe},
overwrite=False,
)
index = VectorStoreIndex.from_vector_store(vector_store=milvus_store)
query_engine = index.as_query_engine()
response = query_engine.query(prompt)
return response.responseEvaluation
Measure and monitor model quality using a range of automated metrics and manual feedback. This helps assess how well your models—including RAG apps—are performing against expected outcomes.
You can run both offline and online evaluations on the traces recorded with Union:
- Online evaluations: Set up a cron job to run evaluations on a regular cadence.
- Offline evaluations: Manually trigger the job and backfill past traces for evaluation.
@union.task(
secret_requests=[...],
container_image=arize_image,
)
def evaluate_rag_arize(
arize_space_id: str,
arize_model_id: str,
model_app_name: str,
backfill_from_datetime: Optional[str] = None,
backfill_to_datetime: Optional[str] = None,
):
from arize.exporter import ArizeExportClient
from arize.pandas.logger import Client
from arize.utils.types import Environments
from phoenix.evals import LiteLLMModel, llm_classify
export_client = ArizeExportClient()
if backfill_from_datetime and backfill_to_datetime:
start_time = datetime.fromisoformat(backfill_from_datetime)
end_time = datetime.fromisoformat(backfill_to_datetime)
else:
end_time = datetime.now()
start_time = end_time - timedelta(
minutes=CRON_MINUTE, seconds=10
)
response_df = export_client.export_model_to_df(
space_id=arize_space_id,
model_id=arize_model_id,
environment=Environments.TRACING,
start_time=start_time,
end_time=end_time,
)
...
remote = UnionRemote(
default_project=union.current_context().execution_id.project,
default_domain=union.current_context().execution_id.domain,
)
app_remote = remote._app_remote
app_idl = app_remote.get(name=model_app_name)
url = app_idl.status.ingress.public_url
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "abc"
eval_model = LiteLLMModel(
model=f"openai/{MODEL_ID}",
model_kwargs={"base_url": f"{url}/v1"},
)
relevance_eval_df = llm_classify(
dataframe=response_df,
template=RELEVANCE_EVAL_TEMPLATE,
model=eval_model,
rails=RELEVANCE_RAILS,
provide_explanation=True,
include_prompt=True,
concurrency=4,
)
correctness_eval_df = llm_classify(
dataframe=response_df,
template=CORRECTNESS_EVAL_TEMPLATE,
model=eval_model,
rails=CORRECTNESS_RAILS,
provide_explanation=True,
include_prompt=True,
concurrency=4,
)
...
arize_client = Client(space_id=arize_space_id, api_key=os.getenv("ARIZE_API_KEY"))
arize_client.log_evaluations_sync(
relevance_eval_df,
project_name=arize_model_id,
verbose=True,
)
arize_client.log_evaluations_sync(
correctness_eval_df,
project_name=arize_model_id,
verbose=True,
)@union.workflow
def arize_online_evaluation(...):
evaluate_rag_arize(...)union.LaunchPlan.get_or_create(
name="arize_online_evaluation_lp",
workflow=arize_online_evaluation,
default_inputs={"arize_space_id": "<YOUR_SPACE_ID>"}, # TODO: Input space_id
schedule=CronSchedule(schedule=f"*/{CRON_MINUTE} * * * *"),
auto_activate=True,
)We use LaunchPlan to define a scheduled execution plan for the evaluation workflow.
In this example, we schedule the job to run every 5 minutes and log results to Arize.
To trigger the Arize evaluation, run the following commands:
# initial backfill
union run --remote --project <YOUR_PROJECT_NAME> evaluation.py arize_online_evaluation \
--arize_space_id "<YOUR_SPACE_ID>" \
--backfill_from_datetime "2025-01-03T01:10:26.249+00:00" \
--backfill_end_datetime "2025-01-15T01:19:27.249+00:00"# generate evals every 5 minutes
# before registering, add your arize space ID to the `evaluation.py` file
union register evaluation.pyPhoenix evaluations follow the same structure as Arize. To trigger the Phoenix evaluation, run the following commands:
# initial backfill
union run --remote --project <YOUR_PROJECT_NAME> evaluation.py phoenix_online_evaluation \
--backfill_from_datetime "2025-01-03T01:10:26.249+00:00" \
--backfill_end_datetime "2025-01-15T01:19:27.249+00:00"# generate evals every 5 minutes
union register evaluation.pyYou can find the end-to-end Arize and Phoenix evaluation code snippets in
evaluation.py.